[Topics] Associate Professor Yasuhiro Morita and his research team aim to build a resource-circulating, low-impact livestock system using wood ear mushrooms
Combining Mushroom Cultivation and Livestock under Solar Sharing
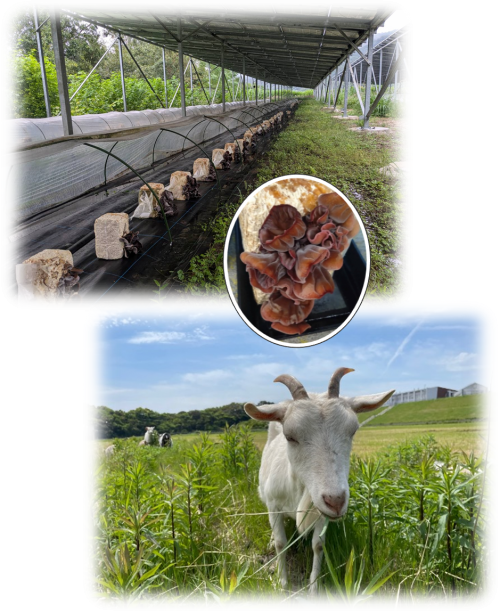

A research group led by Associate Professor Yasuhiro Morita of the Division of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University (University Farm) has launched a collaborative study with Sasaki Co., Ltd. to establish a resource-circulating and eco-friendly livestock system using the wood ear mushroom (Auricularia auricula-judae). In this study, the team will feed A. auricula-judae--a mushroom increasingly cultivated under agrivoltaic (solar-sharing) systems--to ruminant animals such as goats and cattle. The aim is to stimulate beneficial microorganisms in their digestive tracts, thereby improving animal health and feed utilization efficiency. This approach is expected to achieve both higher livestock productivity and reduced environmental impact. Through this research, the team seeks to establish a sustainable, low-impact livestock production model that connects the renewable energy and livestock industries within a resource-circulating regional economy.
Background and Objectives
Ruminant animals emit greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming, making it a major challenge for the livestock industry to reduce the overall environmental impact of production systems. In addition to improving productivity, the industry is now expected to adopt sustainable and eco-friendly management practices.
In livestock production, agrivoltaic (solar-sharing) systems have been introduced, and attempts have been made to grow forage crops or conduct grazing beneath solar panels. However, due to limitations in sunlight conditions and equipment layout, the practical implementation of such systems has been challenging.
In contrast, mushrooms, which thrive in shaded environments, are well suited for cultivation under solar panels, and their production has been rapidly expanding. Among them, the wood ear mushroom (Auricularia auricula-judae), which has seen rising demand but limited domestic production, has become increasingly cultivated in Japan due to its ease of cultivation.
This mushroom is rich in polysaccharides and other functional compounds, and when used as feed for ruminant animals, it is expected to improve the balance of the gut microbiome, thereby enhancing animal health, feed efficiency, and overall productivity, while also reducing environmental impact.
Researcher's Comment
The project aims to develop a carbon-neutral dairy farming model that combines renewable energy initiatives with low-environmental-impact livestock production through mushroom cultivation, and expand this model internationally, particularly in Asian region.
Contact Information
Yasuhiro Morita, Associate Professor
TEL: 092-802-4531
Mail: morita.yasuhiro.362★m.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Please replace ★ with @ in the email address











 Contact
Contact
 Access Map
Access Map

